What Are 404 Errors and Why Do They Matter?
404 errors mean the server is unable to locate the requested resource. When visitors click on a broken link or type an incorrect URL, they encounter this frustrating “Page Not Found” message. These errors occur when pages are removed, relocated, or when URLs are entered incorrectly.
Knowing how 404 errors work is important, as they affect your website’s overall performance. While 404 errors on your site generally do not negatively impact your site’s search ranking in Google, they can still cause problems. 404 errors often raise a website’s bounce rate since users usually exit when they land on broken pages.
Common Causes of 404 Errors
Internal Link Issues
- Deleted pages without proper redirects.
- Typos in internal links.
- Changed URLs without updating references.
- Broken navigation menus.
External Link Problems
External 404s happen when your site points to content on other websites that has been removed or relocated without a proper 301 redirect in place. These broken outbound links can hurt your site’s credibility.
Server and Technical Issues
- Server configuration problems.
- Incorrect file permissions.
- Database connection errors.
- Plugin conflicts on WordPress sites.
How to Find 404 Errors on Your Website?
Using Google Search Console
Google Search Console provides the most reliable way to identify 404 errors affecting your site. Navigate to the Coverage report to see which pages are returning 404 status codes.
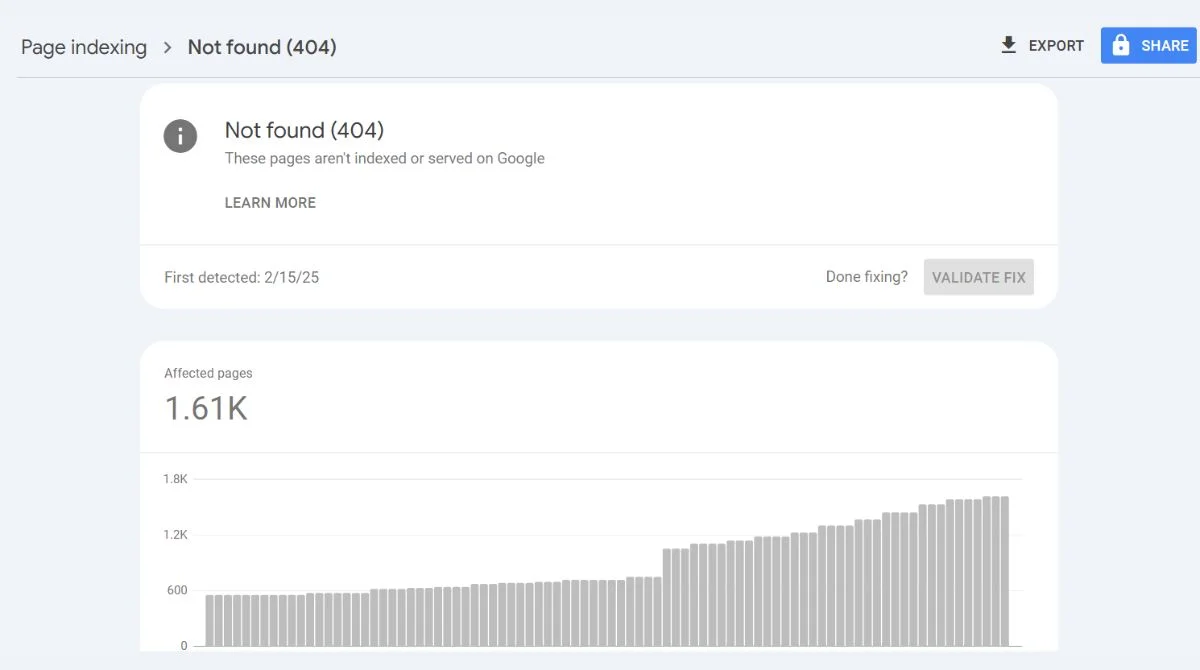
Website Crawling Tools
Use tools like Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to crawl your entire website and identify broken links. These tools can find both internal and external 404 errors.
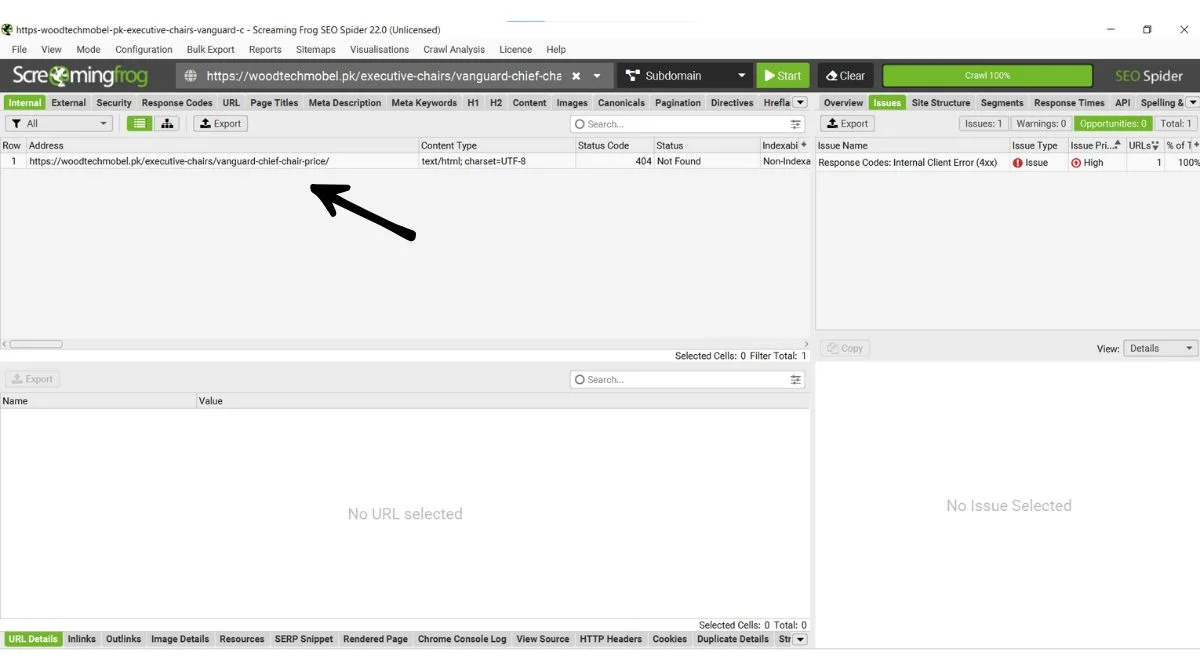
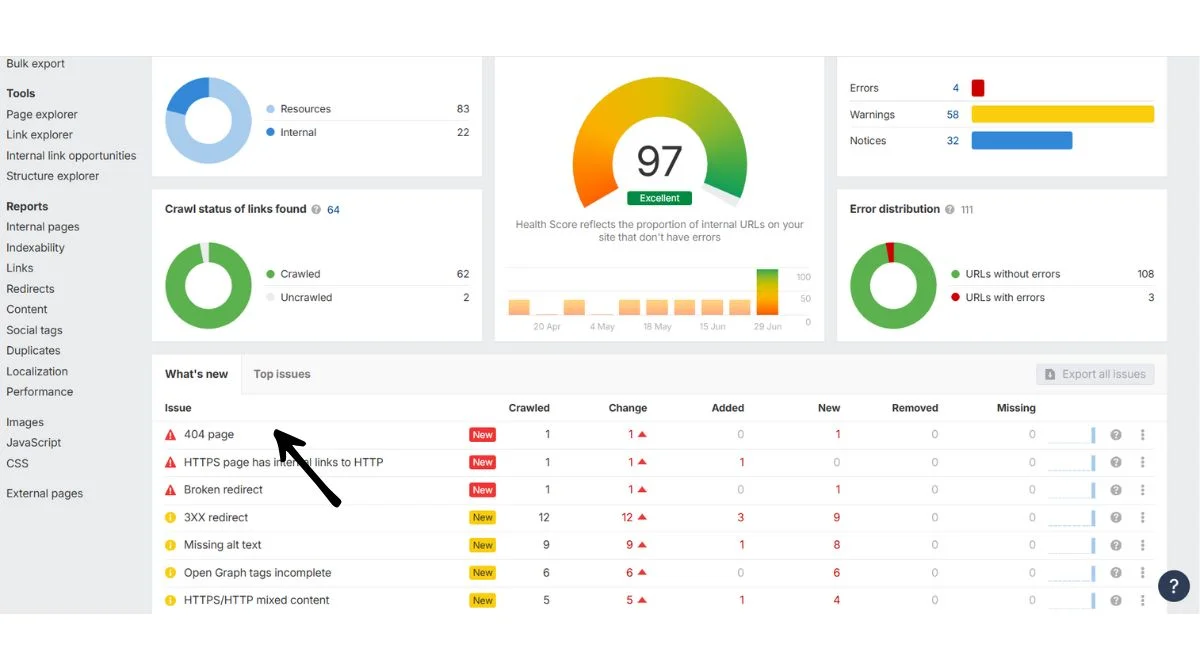
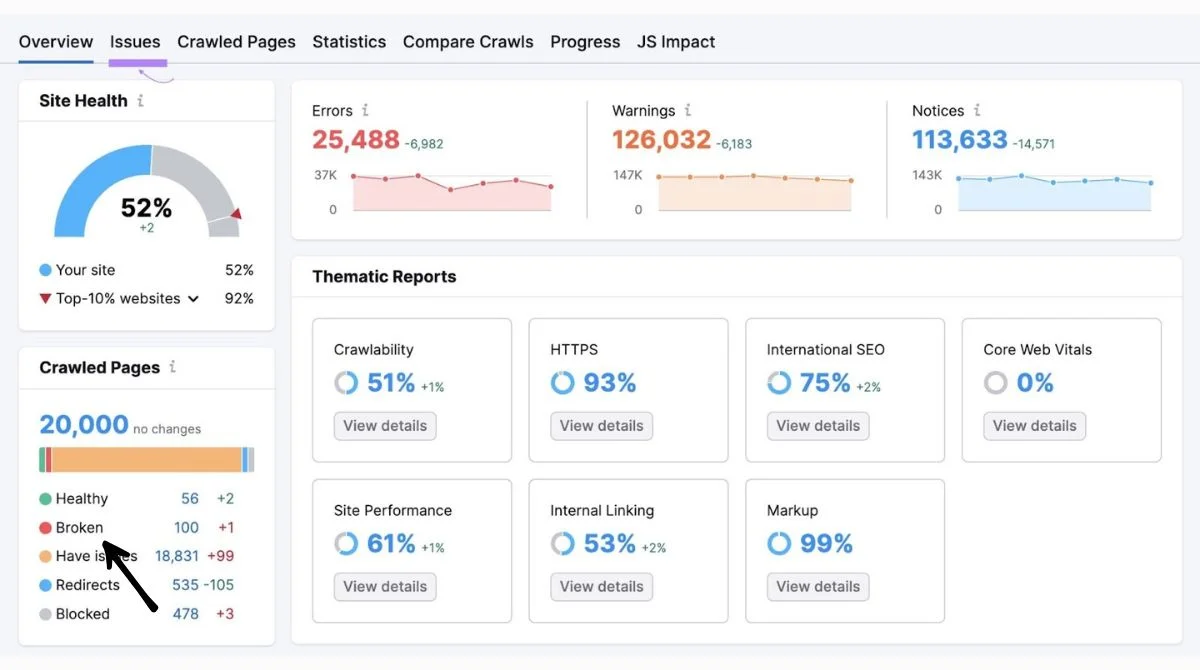
Manual Testing
Regularly test your website’s navigation, forms, and important pages. Check that all links work properly and lead to the correct destinations.
Server Log Analysis
Review your server logs to identify frequently requested URLs that return 404 errors. This helps prioritize which broken links need immediate attention.
Step-by-Step Guide to Fix 404 Errors
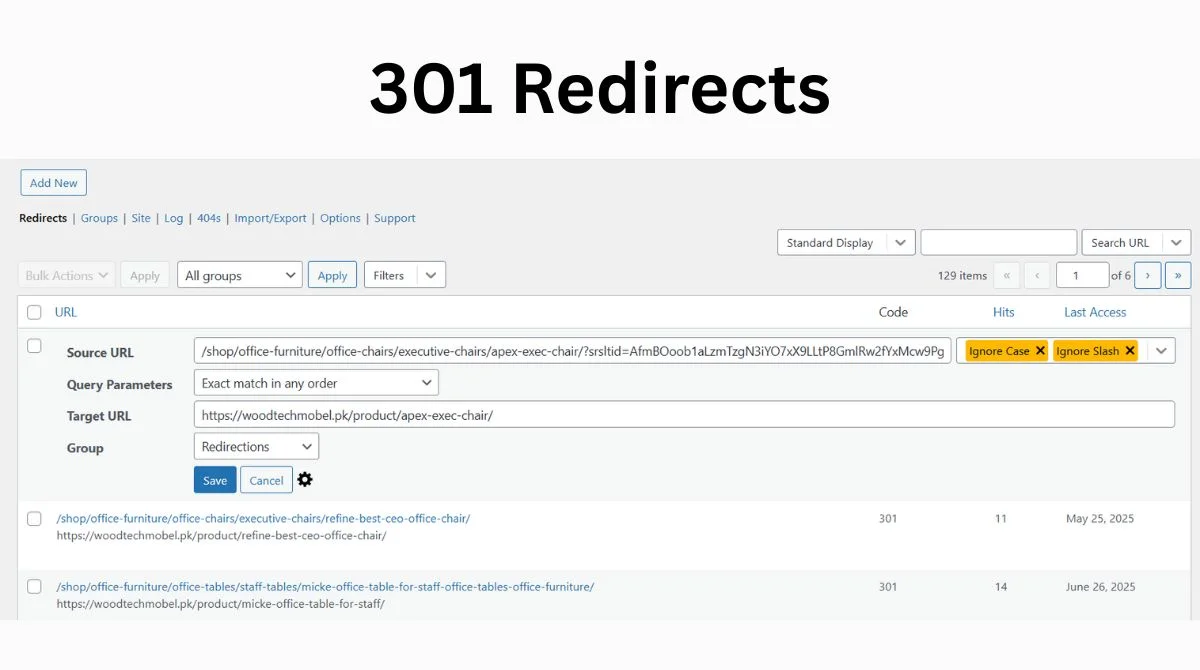
Method 1: Set Up 301 Redirects
The main (free) way to fix 404 errors is to set up a 301 redirect, which is a permanent redirection from a broken URL to a working URL. This method works best when you have moved content to a new location.
How to implement 301 redirects:
- Access your .htaccess file (for Apache servers).
- Add redirect rules for each broken URL.
- Test the redirects to ensure they work correctly.
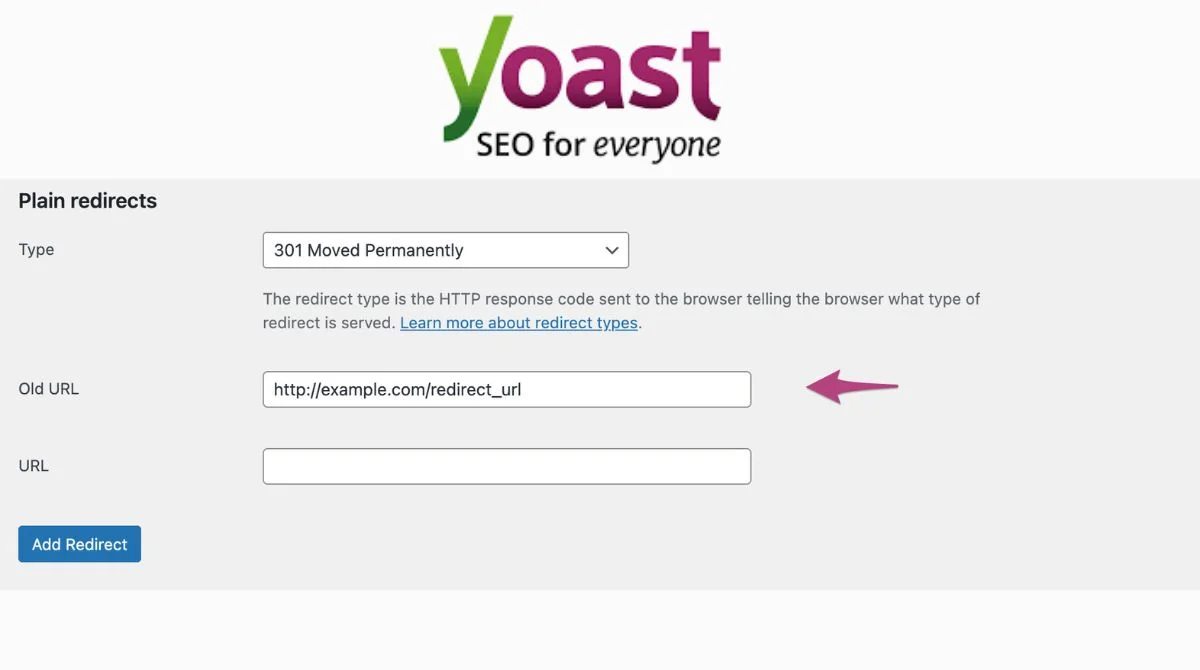
Using SEO Plugins for Easy Redirects
WordPress users can simplify redirect management using popular SEO plugins:
Yoast SEO Plugin
- The premium version includes a redirect manager.
- Automatically creates redirects when URLs change.
- Simple interface for managing redirects.
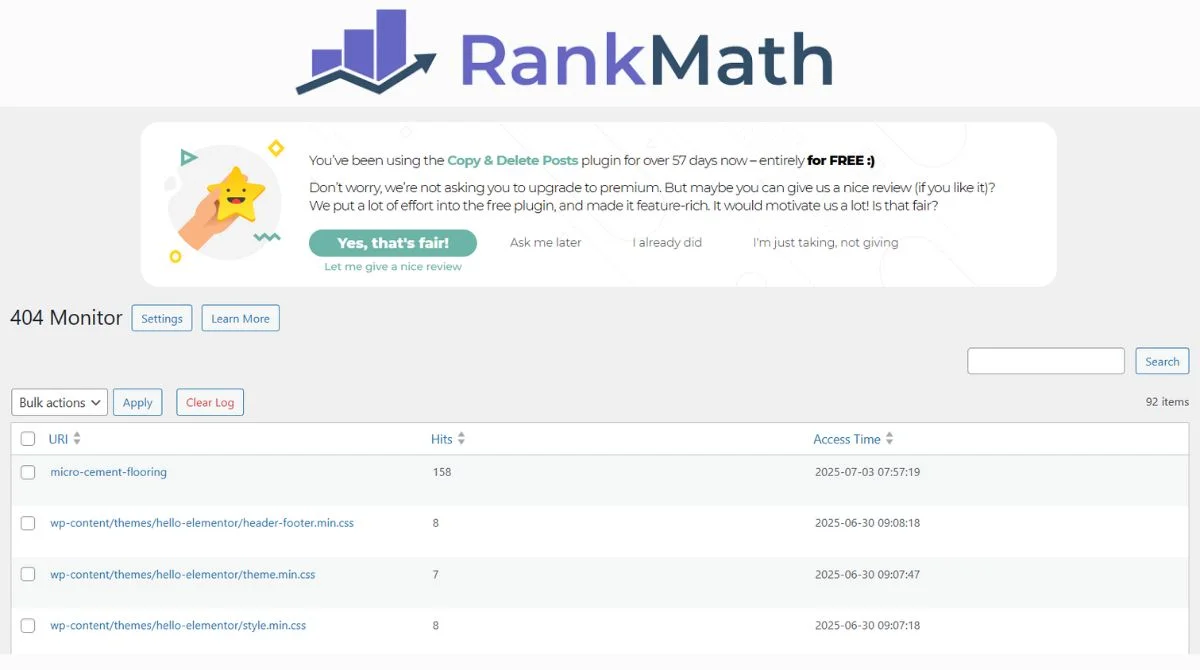
RankMath SEO Plugin
- Built-in redirect manager in the free version.
- Bulk redirect import options.
- Advanced redirect rules and conditions.
Other WordPress Redirect Plugins
- Redirection plugin (free and comprehensive).
- Simple 301 Redirects.
- Safe Redirect Manager.
These plugins eliminate the need for manual .htaccess editing and provide user-friendly interfaces for managing redirects.
Method 2: Restore Deleted Content
Restore deleted webpages as long as there is no business reason to keep them deleted. If the content was accidentally removed and still has value, simply republish it at the original URL.
Method 3: Update Internal Links
Promptly fix these errors by updating invalid links to point to the proper URL or removing the link. Go through your website and update any internal links that point to non-existent pages.
Method 4: Remove Broken Links
When content is gone for good and no replacement fits, the broken links should be removed entirely. This prevents users from encountering dead ends.
Best Practices for Managing 404 Errors
Create a Custom 404 Page
Design a helpful 404 page that provides value to users instead of showing a generic error message. Include:
- Clear explanation of what happened.
- Search functionality.
- Links to popular pages.
- Contact information.
- Navigation menu.
Regular Website Monitoring
Set up automated monitoring to detect new 404 errors as they occur. Tools like Google Search Console send notifications when new crawl errors are discovered.
Implement Proper URL Structure
Use clear, descriptive URLs that are less likely to change over time. Avoid using dates or temporary identifiers in your URL structure.
Test Before Publishing
Always test new content and links before making them live. This prevents publishing broken links that could create 404 errors.
Google’s Guidelines for 404 Errors
Google advises letting 404s stand for pages that were deleted without a replacement or for incorrect URLs that were never part of your site. Redirect commonly misspelled or alternatively spelled URLs to the correct page.
Google makes it clear that most 404 errors aren’t worth fixing, as they generally don’t affect your site’s indexing or rankings. Focus your efforts on fixing 404 errors that impact user experience or have inbound links pointing to them.
When 404 Errors Can Impact SEO?
Loss of Link Equity
404 errors can cause loss of link equity. You can reduce the impact by creating proper redirects that pass link equity to the most relevant pages. This is particularly important for pages with valuable backlinks.
User Experience Impact
When visitors hit these errors, they’re likely to leave your site, which increases bounce rates. Search engines pick up on this, and it can hurt your SEO performance.
External Links to 404s
If your site contains links to external pages that lead to 404 errors, it can have a negative effect on your search rankings. Regularly audit your outbound links to ensure they’re still working.
Tools to Monitor and Fix 404 Errors
Free Tools
- Google Search Console.
- Google Analytics.
- Broken Link Checker plugins.
- Online broken link checkers.

Premium Tools
- Ahrefs Site Audit.
- SEMrush Site Audit.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider.
- DeepCrawl.

Prevention Strategies
Content Management
- Document all URL changes.
- Use version control for website updates.
- Create content archival policies.
- Regular content audits.
Technical Implementation
- Implement proper redirects before deleting content.
- Use canonical URLs consistently.
- Set up monitoring alerts.
- Regular website backups.
When to Seek Professional Help?
Complex 404 error issues may require technical expertise. Consider professional help when:
- Server configuration problems persist.
- Large-scale website migrations are needed.
- Custom redirect solutions are required.
- Technical SEO audits are necessary.
For comprehensive technical support and website optimization, visit RhinoClicks to get expert assistance with resolving 404 errors and improving your website’s performance.
Conclusion
Managing 404 errors effectively requires a balanced approach. While not all 404 errors harm your SEO, addressing those that impact user experience and link equity is crucial. Regular monitoring, proper redirects, and preventive measures will keep your website running smoothly and maintain positive user experiences. Keep in mind that 404 errors don’t directly impact your SEO rankings, but they can influence user experience and your site’s credibility. Focus on fixing the errors that matter most to your users and business goals.